14.JAVA data types
Java data types - integer data 整数数据
Integers (to non-mathematicians) are whole numbers, numbers with no fractional part, no decimal point.
以下四种:
以下四种:
1.byte
8 bits -128 to 127 (0 to 255)
Bytes. e.g., individual bytes of image data; in 32 bit images there is 1 byte each for red, green, blue and alpha (transparency)
字节数。例如,图像数据的单个字节;
在32位图像中,红、绿、蓝和alpha(透明度)各有一个字节
Bytes. e.g., individual bytes of image data; in 32 bit images there is 1 byte each for red, green, blue and alpha (transparency)
字节数。例如,图像数据的单个字节;
在32位图像中,红、绿、蓝和alpha(透明度)各有一个字节
2.short
16 bits -32,768 to 32,767
To save memory – instead of int. However, in most JVMs they are 32-bit anyway, so useless.
要保存内存-而不是int。然而,在大多数jvm中,它们都是32位的,非常没用。
To save memory – instead of int. However, in most JVMs they are 32-bit anyway, so useless.
要保存内存-而不是int。然而,在大多数jvm中,它们都是32位的,非常没用。
3.int (default)
32 bits -2^31 to 2^31 - 1
Everything except very big/very negative values. This is the default.
除了非常大的/非常负的值。这是默认值。
Everything except very big/very negative values. This is the default.
除了非常大的/非常负的值。这是默认值。
4.long
64 bits -2^63 to 2^63-1
long bigNumber = 300000000000000000L;
You will probably use
int 95%+ of the time, long sometimes, and byte occasionally.
实用度 int>long>byte
long bigNumber = 300000000000000000L;
You will probably use
int 95%+ of the time, long sometimes, and byte occasionally.
实用度 int>long>byte
Java data types - floating point非整数
1.float
32 bits
+-10^38 approx.
7 significant digits (decimal) float f = 1.375f;
+-10^38 approx.
7 significant digits (decimal) float f = 1.375f;
2.double
64 bits +-10^38 approx. 15 significant digits (decimal) Default
e.g.
int a = 1000000000;
long b = 1000000000000000000l;
double c = 31.32;
float d = 31.01f;
e.g.
int a = 1000000000;
long b = 1000000000000000000l;
double c = 31.32;
float d = 31.01f;
Java data types - Strings 字符串
As introduced last week, can also use Strings
Strings
String are objects, and have many methods
○ At basic level, can store text data
○ Note, double quotes needed around string
E.g. String str = "This is a String";
○ At basic level, can store text data
○ Note, double quotes needed around string
E.g. String str = "This is a String";
Char
represents a character ('a', 'b', 'c', etc)
A different data type
includes non-Roman characters (Chinese, Cyrillic, Arabic, Greek etc)
○ It is actually a 16 bit integer, range 0 - 65,535
A different data type
includes non-Roman characters (Chinese, Cyrillic, Arabic, Greek etc)
○ It is actually a 16 bit integer, range 0 - 65,535
Java data types - Boolean
Boolean
● We can also store True/False information
● Boolean (means true or false)
Discussed later in the module
Cannot store anything except this
Very useful for checking if conditions are met
Its size varies; it only uses 1 bit, but can take up to 32 bits of memory!
boolean bool = false;
● Boolean (means true or false)
Discussed later in the module
Cannot store anything except this
Very useful for checking if conditions are met
Its size varies; it only uses 1 bit, but can take up to 32 bits of memory!
boolean bool = false;
15.Assigning variables
declaration 存在此变量不占用空间
definition 为变量分配空间 (通常这两个过程是一起的)
initialization初始化 定义后需要一个确定的初始化过程(从无到有)
assignment 赋值 给予一个数值(从有到有)
Instantiate 实例化 把用类创建对象的过程称为实例化。是将一个抽象到具体的过程
Assigning different types of variables We can declare and assign separately
definition 为变量分配空间 (通常这两个过程是一起的)
initialization初始化 定义后需要一个确定的初始化过程(从无到有)
assignment 赋值 给予一个数值(从有到有)
Instantiate 实例化 把用类创建对象的过程称为实例化。是将一个抽象到具体的过程
Assigning different types of variables We can declare and assign separately
int intNum; // declare a variable (assigned a default value) ①
intNum = 22; // assign a new value ②
①+② int intNum = 22; // initialize
double doubNum = 22.0;
float floatNum = 12.3f;
String strData = "Twenty two";
boolean boolData = true;
char charVal = 'c';
16.Arithmetic operators 算子
Operator Description
+ Addition operator(also used for joining Strings) (called String concatenation) 连接算符
- Subtraction operator
* Multiplication operator
/ Division operator
% Modulo (remainder) operator(取余)
++ 自增 +1 --自减 -1
17.Java Arithmetic 计算实战
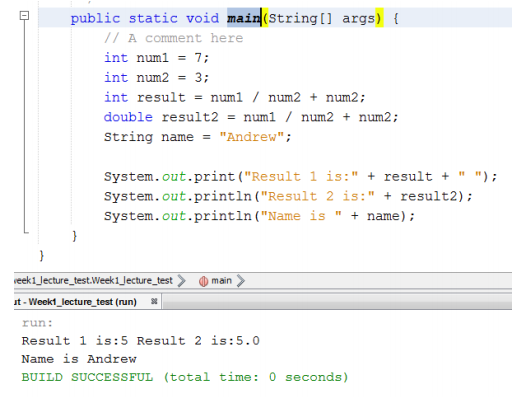
①int num1 = 3;
int num2 = 4;
int result = num1 / num2 ;
System.out.println(result);
Result = 0 //Remember, integers can only use whole numbers
②double num1 = 3;
double num2 = 4;
double result = num1 / num2 ;
System.out.println(result);
Result = 0.75
③double num1 = 7;
double num2 = 3;
double result = num1 / num2;
System.out.println(result);
Result = 2.3333333333333335
④int num1 = 7;
int num2 = 3;
int result = num1 / num2;
System.out.println(result);
Result = 2
/* Why? Because an integer can only store whole
numbers
○ Anything after the decimal point is simply ignored
○ Can cause coding errors, but can also be useful…
浮点精度(float、double)运算不精确的原因 */
⑤int num1 = 7;
int num2 = 3;
int result = num1 / num2;
System.out.println(result) //ignore the decimal point
Result = 2
⑥int num1 = 7;
int num2 = 4;
int result = num1 % num2;
System.out.println(result); //calculate the remainder
Result = 3
⑦int num1 = 7;
int num2 = 3;
int result = num1 / num2 + num2;
System.out.println(result);
Result = 5
⑧int num1 = 7;
int num2 = 3;
int result = num1 / (num2 + num2);
System.out.println(result); //⑦&⑧:order different
Result = 1
*Operator Precedence
First 1.++ -- 2.() 3.* / % 4. + - Last18.Unary Operators
++ Increment operator; increments a value by 1
-- Decrement operator; decrements a value by 1
a -= 3; a = a - 3;
a *= 3; a = a * 3;
-- Decrement operator; decrements a value by 1
int a;
a = 41;
a++;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
a--;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
Output=
a = 42
a = 41
// Another way of expressing it
a -= 3; a = a - 3;
a *= 3; a = a * 3;
19.mathematical function
Such as Square root, Random numbers
有一说一,很多时候平方不如直接做乘法,因为可能会因为精度不够造成错误结果。
有一说一,很多时候平方不如直接做乘法,因为可能会因为精度不够造成错误结果。
double root = Math.sqrt(num)//平方
double root = Math.max(num1,num2);//取大值
double rand = Math.random()
/*will be between 0.0 and 1.0, but not including 1.0, in set symbol [0.0, 1.0).
If you want to expand the range, you can use multiply*/
| Method | Description | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
| acos(x) | Returns the arccosine of x, in radians | double |
| asin(x) | Returns the arcsine of x, in radians | double |
| atan(x) | Returns the arctangent of x between -PI/2 and PI/2 radians | double |
| exp(x) | Returns the value of E^x | double |
| expm1(x) | Returns e^x-1 | double |
| floor(x) | Returns the value of x rounded down to its nearest integer | double |
| hypot(x, y) | Returns sqrt(x^2 +y^2) without intermediate overflow or underflow | double |
| log(x) | Returns the natural logarithm (base E) of x | double |
| max(x, y) | Returns the number with the highest value | double|float|int|long |
| min(x, y) | Returns the number with the lowest value | double|float|int|long |
| pow(x, y) | Returns the value of x to the power of y | double |
| random() | Returns a random number between 0 and 1 | double |
| round(x) | Returns the value of x rounded to its nearest integer | int |
| signum(x) | Returns the sign of x | double |
| sin(x) | Returns the sine of x (x is in radians) | double |
| sqrt() | Returns the square root of x | double |
| tan(x) | Returns the tangent of an angle | double |
| toDegrees(x) | Converts an angle measured in radians to an approx. equivalent angle measured in degrees | double |
| toRadians(x) | Converts an angle measured in degrees to an approx. angle measured in radians | double |
20.Triangles - Hypotenuse
Pythagorean theorem
| Method | Description | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
| hypot(x, y) | Returns sqrt(x^2 +y^2) without intermediate overflow or underflow | double |
| pow(x, y) | Returns the value of x to the power of y | double |
| sqrt(x) | Returns the square root of x | double |
/* pow(x,y) = x^y
hypot(x,y) = sqrt(x^2+y^2)
Sqrt(a) =√a*/
double a = 4;
double b = 3;
double c = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a,2) + Math.pow(b,2));
System.out.println("Value of C is " + c);
Output: Value of C is 5
21. Angles of triangle
● Can use SOH CAH TOA
● SOH = Sin – Opposite and Hypotenuse
● CAH = Cos – Adjacent and Hypotenuse
● TOA = Tan – Opposite and Adjacent
asin acos atan 反三角函数
toDegrees(x) 弧度转角度
toRadians(x) 角度转弧度
● SOH = Sin – Opposite and Hypotenuse
● CAH = Cos – Adjacent and Hypotenuse
● TOA = Tan – Opposite and Adjacent
asin acos atan 反三角函数
toDegrees(x) 弧度转角度
toRadians(x) 角度转弧度
double opp = 2;
double adj = 4;
double val = Math.atan(opp/adj);
double deg = Math.toDegrees(val);
System.out.println("Angle is " + deg);
22.Initial Programming
23.The Scanner Object
The Scanner object is a useful way to receive the System.input
character stream, i.e. accessing characters that you type.
Like a String, a Scanner is an object (we will discuss this in future weeks)
It contains a number of useful methods
Its purpose is to receive and handle keyboard input.
It is a very useful way to provide input to your program.
It wraps your character stream into a Scanner object, which has methods you can use to access it.
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
We can then use it to receive and store an input
String next = kb.nextLine();
Useful to use a System.out to prompt user Input can be stored as a variable and used
System.out.println("Name is " + next );
add import for java Using Package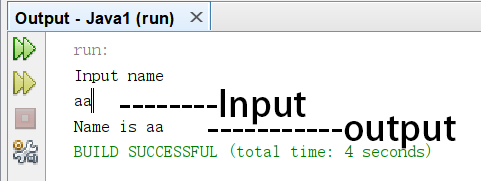
Scanner for keyboard
We can create a new Scanner object easily:Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
We can then use it to receive and store an input
String next = kb.nextLine();
Useful to use a System.out to prompt user Input can be stored as a variable and used
System.out.println("Name is " + next );
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Input name");
String next = kb.nextLine();
System.out.println("Name is " + next);
add import for java Using Package

24.Convert data type
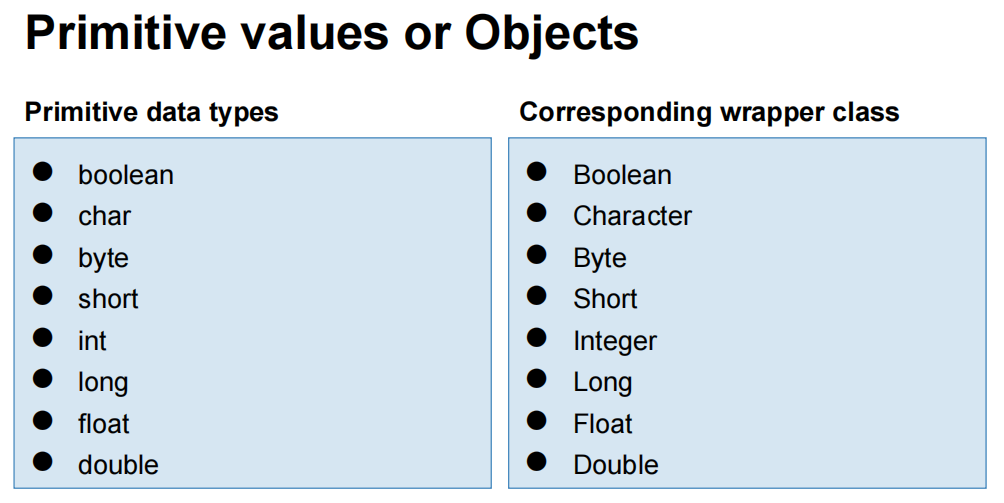
● In fact, there are classes for ALL
primitive data types
● They are called ‘wrapper classes’.
● They are called ‘wrapper classes’.
String s = "999"
int res = Integer.parseInt(s);
String s = "99.021"
double res = Double.parseDouble(s);
boolean x = false;
String m = Boolean.toString(x);
// 此种代码的作用就是把字符串转化为对应的数据类型 前提是转化的数据
public static int getDice() {
double rand = (Math.random() * 6);
int r = (int) rand;
return r;
}
算子int
y = (int) x // 此类算式就是正常的取整计算 结合上文的计算 Scanner Inputpublic static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Input a number");
String next = kb.nextLine();
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(next);
}
● We can convert our String to an integer or double!
● Get input from Scanner
● Run a conversion, store as integer
Variant: (using two inputs for addition, output and)
● Get input from Scanner
● Run a conversion, store as integer
Variant: (using two inputs for addition, output and)
// 变式:(采用两个输入做加法,输出和)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in); //建立一个scanner Input输入
System.out.println("Input a number"); //提示输入
String next = kb.nextLine(); //下一行输入
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(next); //输入1
System.out.println("Input a number"); //提示输入
String next2 = kb.nextLine(); //下一行输入
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(next2); //输入2
int res = num1+num2; //进行加法
System.out.println("Total is " + res); //输出结果
}
25.Good programming style
● Your programming code must be easily read by others and by
yourself.
● This saves time during program maintenance.
● It also leads to less human induced error.
● In software development projects, maintenance often accounts for 80% of effort.
● Program readability is of utmost importance.
就是说一个好的格式能事半功倍,包括空白行、空格、变量的代称、说明等。
/* ... */多行注释
//单行注释
Add blank lines to Improve readability
添加空白行以提高可读性
Put a space between each term
在每个术语之间放一个空格
importHtml 规定的缩写首字母大写 importHTML
message 不要用日常的缩写 msg
● This saves time during program maintenance.
● It also leads to less human induced error.
● In software development projects, maintenance often accounts for 80% of effort.
● Program readability is of utmost importance.
就是说一个好的格式能事半功倍,包括空白行、空格、变量的代称、说明等。
/* ... */多行注释
//单行注释
Add blank lines to Improve readability
添加空白行以提高可读性
Put a space between each term
在每个术语之间放一个空格
importHtml 规定的缩写首字母大写 importHTML
message 不要用日常的缩写 msg
26.Lab learning
Write a Java program that takes two input integers, min and max, from the user, and
generate two random integers between min and max, inclusive
After that, print two two random integers and report whether one is smaller, equal to, or larger than the other
Use boolean value (true or false) to report the comparison between the two random integers
Your program’s input/output interaction should look like:

Boolean can just output true/false.
Boolean Specifies whether it is true or false, just like if.
Use boolean value (true or false) to report the comparison between the two random integers
Your program’s input/output interaction should look like:

Boolean can just output true/false.
Boolean Specifies whether it is true or false, just like if.
Math
Math.round () 四舍五入函数,
(int) Math.round() 四舍五入后转化为整数类型。
Math:这是Java标准库中的一个类,它包含了各种数学函数和常数。
round():这是Math类中的一个方法,用于将一个浮点数值四舍五入到最接近的整数。例如,如果你有一个浮点数值 3.6,Math.round(3.6) 将返回 4。
(int):这是一个类型转换操作符,用于将一个值从一种数据类型(在这种情况下是浮点数)转换为另一种数据类型(在这种情况下是整数)。
Math.Pi: 调用π的值
In second lab, we use the (int) Math.round() to change the double type to integer type.
Also don’t forgot how to change string to int/double.
(int) Math.round() 四舍五入后转化为整数类型。
Math:这是Java标准库中的一个类,它包含了各种数学函数和常数。
round():这是Math类中的一个方法,用于将一个浮点数值四舍五入到最接近的整数。例如,如果你有一个浮点数值 3.6,Math.round(3.6) 将返回 4。
(int):这是一个类型转换操作符,用于将一个值从一种数据类型(在这种情况下是浮点数)转换为另一种数据类型(在这种情况下是整数)。
Math.Pi: 调用π的值
In second lab, we use the (int) Math.round() to change the double type to integer type.
Also don’t forgot how to change string to int/double.
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(next);
double num2 = Double.parseDoule(next);
27.CW1&CW2 learning
A bit A byte A kilobyte A megabyte A gigabyte A terabyte From small to large
Java is a high level language which means that it looks similar to C++ and is easier for humans to read compared to low level languages such as assembly . All Java programs run inside the Java Virtual Machine. Programmers write the source code in Java and then the compiler turns this into a file containing bytecode . The Java Virtual Machine then works as a/an interpreter when it is running the program.
JAVA编程中source code和bytecode有什么区别
编译器和解释器之间有什么区别
int i =10;
The variable i is both declared and initialised.
Java is a high level language which means that it looks similar to C++ and is easier for humans to read compared to low level languages such as assembly . All Java programs run inside the Java Virtual Machine. Programmers write the source code in Java and then the compiler turns this into a file containing bytecode . The Java Virtual Machine then works as a/an interpreter when it is running the program.
JAVA编程中source code和bytecode有什么区别
编译器和解释器之间有什么区别
int i =10;
The variable i is both declared and initialised.







Comments NOTHING